Hemorrhagic Stroke
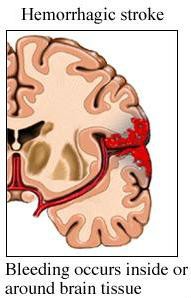
A hemorrhagic stroke is caused by a hemorrhage or sudden bleeding into or next to the brain. This problem accounts for 13 percent of strokes. The rest of stroke cases are ischemic strokes. Typically hemorrhagic strokes occur in the brain itself and are called intracerebral hemorrhages. Some patients suffer from bleeding in the fluid filled areas located deeper in the brain which is known as intraventricular hemorrhage or into the small area between the brain and the covering membranes which is known as subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel that supplies the brain ruptures and bleeds. When an artery bleeds into the brain, brain cells and tissues do not receive oxygen and nutrients. In addition, pressure builds up in surrounding tissues and irritation and swelling occur. About 13 percent of strokes are caused by hemorrhage (10 percent are intracerebral hemorrhage and 3 percent are subarachnoid hemorrhage strokes). Hemorrhagic strokes are divided into two main categories, including:
- Intracerebral hemorrhage. Bleeding is from the blood vessels within the brain.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage. Bleeding is in the subarachnoid space (the space between the brain and the membranes that cover the brain).
Causes:
Intracerebral hemorrhage is usually caused by hypertension (high blood pressure), and bleeding occurs suddenly and rapidly. There are usually no warning signs and bleeding can be severe enough to cause coma or death.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage results when bleeding occurs between the brain and the meninges (the membrane that covers the brain) in the subarachnoid space. This type of hemorrhage is often due to an aneurysm or an arteriovenous malformation (AVM).
- An aneurysm is a weakened, ballooned area on an artery wall and has a risk for rupturing. Aneurysms may be congenital (present at birth), or may develop later in life due to such factors as hypertension or atherosclerosis.
- An AVM is a congenital disorder that consists of a disorderly tangled web of arteries and veins. The cause of AVM is unknown.
At Alimran Medical Center, we may recommend any of the following treatments:
Non surgical treatment
Chiropractic
Prolotherapy
Repetitive transcranial magnatic stimulation (rTMS)
Surgical treatment
Craniotomy