Sympathetic nerve block
Lumbar sympathetic block
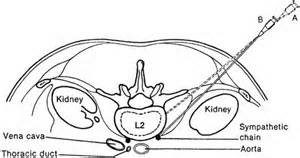
A lumbar sympathetic block is an injection of local anesthetic into the back using X-ray guidance or ultrasound. With this procedure, we are blocking the sympathetic nerves to the leg. These nerves typically are not responsible for sensation, but they can be “turned on” in certain pain syndromes.
This procedure is typically ordered by your doctor for pain located in the buttocks and/or legs that is caused by sympathetically maintained pain, or complex regional pain syndrome, formerly known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD). It may also be ordered for nerve injury or post-herpetic neuralgia (herpes zoster, shingles). Lumbar sympathetic blocks are also used with circulation problems (e.g., vascular insufficiency) to see if blood flow can be improved.
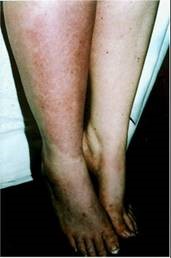
complex regional pain syndrome
Celiac plexus block
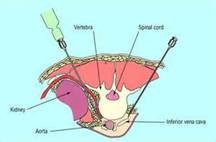
The celiac plexus is a bunch of nerves that supplies the sensation from organs in your abdomen (e.g., pancreas, bowel, etc.). It is used for patients with pain due to abdominal malignancy or chronic pancreatitis.
The plexus is located along the side of your spine. Alcohol is injected to destroy the nerves when a neurolytic block is performed, usually for patients with cancer.
A diagnostic block is often done prior to a neurolytic block to ensure that pain relief can be achieved by this type of injection. Your doctor will tell you if you are an appropriate candidate for a neurolytic block.
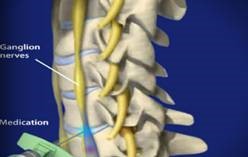
Stellate ganglion block
A stellate ganglion block (sympathetic block) is an injection of local anesthetic into the front of the neck. It is typically ordered by your doctor for pain located in the head, neck, chest or arm that is caused by sympathetically maintained pain (complex regional pain syndrome), causalgia (nerve injury), herpes zoster (shingles) or intractable angina. Stellate ganglion blocks are also used with circulation problems, particularly Raynaud’s or complex regional pain symdrome (CRPS), to see if blood flow can be improved.
Stellate ganglion blocks may be of therapeutic or diagnostic value. One of three things will happen:
The pain does not go away, but there is other evidence of a sympathetic block, meaning the pain is not responsive to sympathetic blocks. This is of diagnostic value.
The pain does not go away and there is no good evidence of a sympathetic block, meaning the block is a technical failure.
The pain goes away after the injection and stays away longer than the life of the local anesthetic, meaning the block was of therapeutic value.
The procedure will most likely have to be repeated to achieve a long-lasting benefit. The spacing of injections will be based on how long the pain relief lasts between injections. Usually, you will experience a longer benefit following each subsequent injection
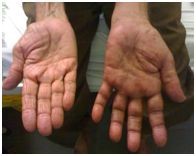
CRPS Left hand
Left Stellate ganglion block –
Superior hypogastric block
A superior hypogastric block is an injection of local anesthetic and steroid around the sympathetic nerves which supply the organs of the pelvis.
These nerves are located on either side of the spine in the lower abdomen. After successful diagnostic injection RF ablation or alcohol neurolysis can be performed to provide long lasting pain reli