Electrical stimulation
What is electrical stimulation?
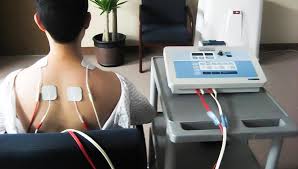
Electrical stimulation or E-stimulation is commonly used in Physiotherapy to help increase the strength of weak muscles and relieve pain. The main advantage of E-stimulation is that it makes use of natural pain relieving mechanisms, and hence has minimal side effects. Drug therapies effectively introduce foreign chemicals to achieve the same end, but in doing so alter your metabolism and bodily function, hence causing more potential side effects. The main use in physiotherapy for E-stimulation is as a means of relieving chronic pain relief without the risk of drug interactions and/or side effects.
E-stimulation devices can provide a range of frequencies, which allow them to tailor to a broad range of physiologies, each of which may respond differently under a range of stimulation. New machines are becoming more compact and easy to use, allowing patients to use the therapy in the comfort and privacy of home after instruction and guidance from a physic. E-stimulation will often be used in conjunction with other forms of physical therapy for the best clinical outcomes. Using the technique in conjunction with hot and cold therapies, hydrotherapy, stretching, and therapeutic exercise is common practice.
Types of E-stimulation:
1-Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a form of electrotherapy which makes use a of a convenient device that applies an electrical current through the skin to stimulate sensory nerves and trigger the release of endorphins, hormones with a pain relieving property that provide a natural and effective relief of chronic pain. TENS is actually quite a broad category describing a range of different techniques based on applying electrical stimulation through the skin, but within physiotherapy, its use is generally focused on the relief of symptomatic pain, particularly in instances of chronic pain that is not being dealt with effectively by means of medication.
2-Interferential therapy (IFT) involves the use of low frequency electricity to stimulate peripheral nerves. Clinically this method is used to reduce oedema (abnormal pooling of blood and/or fluids in body tissue), relieve chronic pain, stimulate muscles, and improve blood flow in a target region. These frequencies stimulate a natural pain relieving mechanism called the Opioid mechanism causing pain free pain relief.
Muscles are innervated with motor neurons that can be stimulated by electricity, the lower the frequency the milder the effect and hence contraction. This stimulus can be controlled in a manner that mimics the natural electrical activity of muscles achieved during exercise. This method is particularly useful for physics treating patients who are unable to achieve active exercise for whatever reason as it prevents muscular degradation and is thought to have a strengthening effect.
What are the benefits of E-stimulation?
- ‘Wakes up’ weak or inactive muscles
- Helps improve muscle strength and endurance
- Helps improve the muscle brain pathways
- Helps increase blood supply
- Helps reduce pain
- Helps with joint movements by helping the associated muscles work better
Contraindications in the use of E-stimulation for physiotherapy
1- Some patients may complain of an allergic reaction either to the electrodes applied to your skin for TENS, or to the adhesive substances used to hold said electrodes in place.
2- Pregnancy means that electrodes should not be applied to the abdomen or surrounding region.
3- Applying any current through the skin whilst harboring an electrical implant like a pacemaker is not advised as the device may interfere with it.
4- Electrodes should not be placed on top of skin that is suffering from a dermatological condition like eczema, infection and wounds.