Stroke and post-stroke recovery
Overview
A stroke is a medical emergency. Immediate treatment is absolutely necessary. Early intervention can reduce brain damage and complications.
Fortunately, strokes can be treated and prevented.
Symptoms
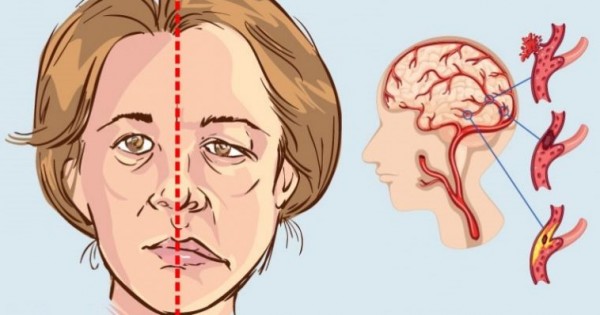
Look for these signs and symptoms if you think you or someone else has a stroke. Be careful when the symptom smiles start. The duration of symptoms can affect treatment options that are available to you:
You may be confused. You may speak out or have difficulty understanding speech.
You may have sudden numbness, weakness or paralysis in your face, arm or leg. This often happens on one side of the body. Try to lift both your arms over your head at the same time. If one of your arms starts to fall, you may have a stroke. One side of the mouth may also fall when you try to smile.
Visual problems in one or both eyes.
Headache.
You may fall off or feel suddenly dizzy, or lose balance or coordination.
The government’s decision
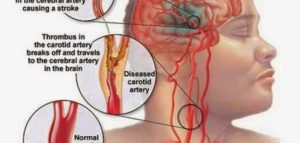
Stroke occurs if there is a problem or defect in the amount of blood coming into the brain. The cause of the most common type of stroke — ischemic stroke — is to deliver a small amount of blood to the brain.
The cause of the other type of stroke – hemorrhagic stroke – is the presence of excess blood in the skull.
There are many causes of a stroke, including:
Cerebral bleeding occurs as a result of a rupture of the wall of blood vessels, this causes high blood pressure, and causes weakness in the blood vessels.
Diseases and heart ailments.
Psychological stress such as fear and anxiety.
Decline in blood circulation.
Drugs, especially cocaine.
Obesity and weight gain.
High cholesterol is bad blood.
Hypertension. Aging.
Constant headache.
Muscle atrophy is possible.
Blurred vision.
Progressive hearing loss.
Imbalance and imbalance.
Heredity.
Risk factors
There are many factors that can increase the risk of stroke. Some factors can increase your chances of having a heart attack. Treatable stroke risk factors include:
Lifestyle risk factors
Overweight or obesity
A dissertation of physical activity
Drinking alcohol or drinking too much
Use of prohibited drugs such as cocaine or methamphetamine
Medical risk factors
Blood pressure readings above 120/80 mm hg (mmHg)
Smoking and smoke inhalation other people ‘smoke’ (second-hand smoke)
High cholesterol
Diabetes
Obstructive sleep apnea
Cardiovascular diseases including heart failure, heart failure, heart infection and abnormal heart rate
Heredity (family history of strokes, heart attacks or transient ischemic attack).
Other factors associated with an increased risk of stroke include:
Age— The age group 55 years and older are at higher risk of stroke than young people.
Race – African Americans are at greater risk of stroke than other races.
Sex – Men are at greater risk of stroke than women. Women are usually older when they have strokes, and are more likely to die from strokes than men.
Hormones – The use of pills or hormone therapy that contains estrogen, in addition to high levels of estrogen due to pregnancy and childbirth.
Complications
Stroke can sometimes cause temporary or permanent disabilities, depending on how long the brain lacks blood flow and the affected part. Complications may include:
Paralysis or loss of muscle movement. Physical therapy may help you restore activities that are paralyzed, such as walking, eating and dressing.
Difficulty speaking or swallowing. Stroke may reduce control over the way the oral and throat muscles move, making it difficult to speak clearly (dysphagia), swallowing or eating (dysphagia). You may also have difficulty speaking (loss of speech ability), including speaking or understanding speech, reading or writing.
Many people who have had strokes feel some amnesia. Others may have difficulty thinking, making judgments, reasoning and understanding terms.
People who have strokes may have more difficulty controlling their emotions, or may develop depression.
People who have strokes may feel pain, numbness or other strange sensations in some parts of their bodies affected by a stroke. For example, if a stroke causes a loss of sensation in your left arm, you may feel an uncomfortable tingling in that arm.
People may also become very sensitive to temperature changes, especially extreme cold, after a stroke. These complications are known as central stroke pain or central pain syndrome. This condition generally develops several weeks after a stroke and may improve over time.
However, because pain is caused by a brain problem, not a physical injury, there are few treatments for this condition.
Changes in behavior and self-care. They may need help taking care of themselves and performing their daily tasks.
Like any brain injury, the success of treating these complications will vary from person to person.
Prevention
Awareness of risk factors and a healthy lifestyle are the right steps to avoid a stroke.
A healthy lifestyle includes:
Treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure)
Reduce consumption of foods rich in cholesterol and fats
Avoid smoking
Diabetes Treatment
Maintaining a healthy weight
Exercise regularly
Treatment of stress
Avoid alcoholic beverages
Avoid drugs
Maintaina a balanced and healthy diet
Treatment
Emergency treatment for a stroke depends on whether you have an ischemic stroke that blocks an artery — the most common type — or a hemorrhagic stroke involving bleeding in the brain.
In general, treatment is done to:
Emergency treatment (hospital recital)
Drug treatment after the period of stability of the patient’s health, which includes:
Treatment of blood pressure and diabetes
Internal brain pressure therapy
Treatment of blood clotting (blood thinners) in the case of ischemic stroke, subject to the necessary conditions
Surgical intervention (blockage of the arteries with the thrombus) where it was greater than 70% less severe and mortality rates with complications of less than 6%.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation
Its purpose is as follows:
Get the injured part back to work.
Reduce dependency on others.
This treatment includes:
(Rehabilitation, physical, adaption, mental, social, functional, speech)
1.Traditional treatment (mechanical)
Teach the patient the correct position when sitting down, lying down.
Treatment of the joints of the injured part
Elongation exercises, strengthening exercises and resistance exercises
2. Physical Therapy
Stimulation of the nerve and muscle damaged in the affected area
Different types of stimulation include: FES, IDC, IF, TENS by case and status.
Cold laser rays, long wave, us, sad
Running and walking exercises (slow-fast)
Bio feed back devices to make the patient more aware of the movement of the affected limb to develop its movement through brain-reaching gestures or the use of mirrors
3. Advanced Devices (Third Line of Treatment)
(non-invasive brain stimulation (rtmsbrain stimulation device
Non-surgical interventions to stimulate the spinal cord epidural stimulation
Mechanical pull device for the spine exposed to disc slippage, nerve pressure and spin MED
VR software (electronic games) for the virtual world helps to move the affected part.
4. Treatstroke complications
Shoulder dislocation
Inflammation and rupture of tendons
Fluid aggregation and swelling
Treatment of spasms (muscle-tendon) and includes injection of local needles using pharmaceutical substances (BOTOX) or Chinese needles.
Bladder weakness and lack of control
Stop speaking or difficultto find words.
Post-stroke depression.