Bed sore
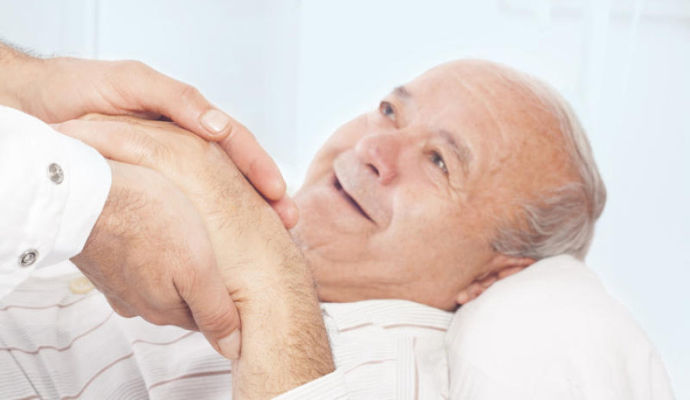
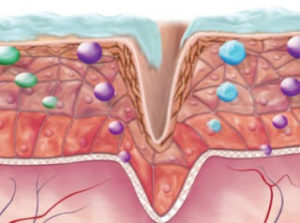 Bed sore (or what is known scientifically as pressure sore ) occurs as a result of constant friction or permanent pressure on a specific area of the body without rest, as in cases of prolonged lying down for patients with paralysis, for example
Bed sore (or what is known scientifically as pressure sore ) occurs as a result of constant friction or permanent pressure on a specific area of the body without rest, as in cases of prolonged lying down for patients with paralysis, for example
Causes of bed sore
According to experts, a bed sore arises when the blood supply to a particular area of the body is interrupted for 2-3 hours, and these are
the reasons for what happens:
- Constant pressure on a specific area of the body.
- Constant friction resulting from constantly fluctuating in the bed and staying in it, for example, in people who suffer from delicacy in the skin or poor blood circulation.
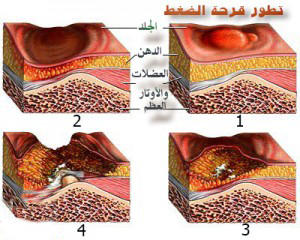 Stages of bed sore
Stages of bed sore
Bed sore usually develops in 4 stages, separated by the following:
Stage 1: The skin in the affected area appears red and warm when touched, with possible itching.
The second stage: ulcers and blisters may appear simple or open, surrounded by an area that differs in color from the skin’s normal color.
The third stage: the appearance of a nozzle-like injury due to the damage that has begun to affect the lower layers of the skin.
Stage 4: Significant damage to the skin tissue with inflammation. Bones or muscles may become visible.
Treating bed sore
Treating a bed sore is not impossible, but it is not easy either. Open wounds do not heal quickly, and when they heal, their recovery may not be regular.
It may take a few weeks to heal, but more advanced wounds may need surgical intervention. Here are the steps to take to treat bed sore:
Decompression of the affected area, by using items such as pillows to lift specific parts of the body.
Cleaning the wound, minor wounds can be cleaned with water and medicinal mild soap. As for the wounds that remain open, these need to be sterilized with saline every time the bandages are changed.
Disposing of dead tissue at the site of the wound, the wound cannot fully recover if it contains dead or inflammatory tissues.
Using bandages, bandages may be needed to protect open wounds from any infection until they are completely healed.
Take antibiotics or use topical fat that contains antibiotics.
Medical intervention in advanced cases may include one of the following:
Reverse pressure by delivering a pump with the sore site to withdraw moisture from the site of infection, reduce the chances of inflammation and accelerate healing.
Surgery, by using a healthy patch of patient’s skin to close the open wound after cleaning it thoroughly.
Although treating bed sores is not impossible, however, the delay in providing the necessary treatment may lead to serious complications in the person who may be fatal.
Who may get bed sore?
Bed sore usually affects people who cannot move freely or are unable to move at all, as in cases of patients with paralysis.
Also, people who depend on a wheelchair also have a higher chance of developing bed ulcers.
Generally speaking, the following factors increase the chances of developing bedsore:
Age.
Decreased ability to feel and feel the different parts of the body.
Poor blood circulation due to diabetes, arterial disease, or smoking.
Bad diet, especially poor diets in the following elements: proteins, vitamin C, zinc.
An impairment of the mental or mental health of the injured person, which reduces his chances of seeking proper care early.
Treating bed sore
Treating a bed sore is not impossible, but it is not easy either. Open wounds do not heal quickly, and when they heal, their recovery may not be regular.
It may take a few weeks to heal, but more advanced wounds may need surgical intervention. Here are the steps to take to treat bed sore:
Decompression of the affected area, by using items such as pillows to lift specific parts of the body.
Cleaning the wound, minor wounds can be cleaned with water and medicinal mild soap. As for the wounds that remain open, these need to be sterilized with saline every time the bandages are changed.
Disposing of dead tissue at the site of the wound, the wound cannot fully recover if it contains dead or inflammatory tissues.
Using bandages, bandages may be needed to protect open wounds from any infection until they are completely healed.
Take antibiotics or use topical fat that contains antibiotics.
Medical intervention in advanced cases may include one of the following:
Reverse pressure by delivering a pump with the sore site to withdraw moisture from the site of infection, reduce the chances of inflammation and accelerate healing.
Surgery, by using a healthy patch of patient’s skin to close the open wound after cleaning it thoroughly.
Possible complications
Without getting proper and timely treatment, bed sore can lead to serious complications such as:
Cellulitis, which may subsequently cause sepsis and infection in all parts of the patient’s body.
Bone and joint infections.
Infection with sepsis or sepsis.
Methods of prevention
Even with providing all the necessary measures to prevent bed sore, it may be difficult, but not impossible, to prevent it completely. Here are the most important simple preventive steps:
Moving the patient in a wheelchair at least once every 15 minutes, and moving the patient in bed at least once every two hours.
Check skin closely every day.
Keeping the skin healthy and dry.
Good nutrition.
Quit Smoking.
Simple exercises according to the patient’s condition.