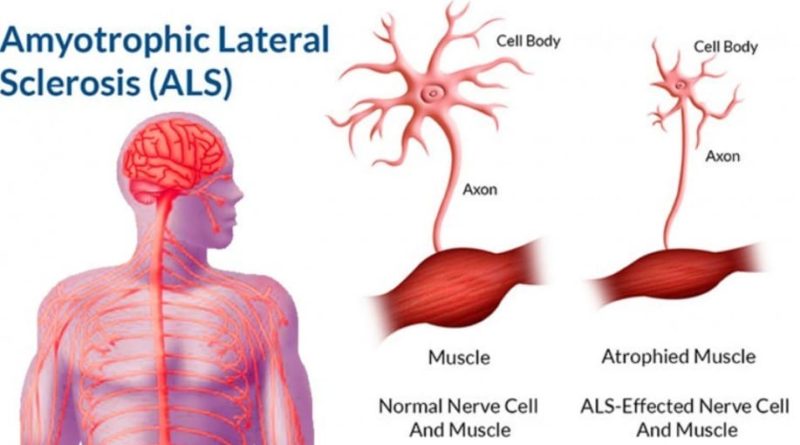
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) has traditionally been described as a disease that manifests as atrophy and progressive weakness of the skeletal, spinal, and bulb muscles due to the degeneration of motor neurons in the anterior medulla horn. and of the corticoespinal system. Sensitive function is generally maintained. It is accompanied by impaired speech (dysarthria) and difficulty swallowing. Emotional lability is also common. As with other progressive neurological diseases, its etiology is still unknown, although it is attributed to a possible viral, toxic, genetic or endocrine cause.
Currently there are no effective drugs that can act during the course of the disease, but there are no drugs that can alleviate the symptoms. However, rehabilitation, with the participation of different professionals and from the earliest stages of the disease, improves the quality of life of these patients.
In more advanced cases, the use of a pacemaker surgically implanted in the diaphragm causes muscle contraction and offers patients with some neuromuscular diseases, such as ALS, dependent on continuous mechanical ventilatory support, the ability to breathe. without mechanical support (after proper training). This represents a significant improvement in their quality of life, a reduction in recurrent respiratory infections and, ultimately, an increase in survival. The Guttmann Institute is a pioneer in the implantation of this type of pacemaker in our country, both in adults and children of very young age (in the latter case, due to high cervical spinal cord injuries), with highly satisfactory results.
In general, treatment is done to:
Emergency treatment (hospital recital)
Drug treatment after the period of stability of the patient’s health, which includes:
Treatment of blood pressure and diabetes
Internal brain pressure therapy
Treatment of blood clotting (blood thinners) in the case of ischemic stroke, subject to the necessary conditions
Surgical intervention (blockage of the arteries with the thrombus) where it was greater than 70% less severe and mortality rates with complications of less than 6%.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation
Its purpose is as follows:
Get the injured part back to work.
Reduce dependency on others.
This treatment includes:
(Rehabilitation, physical, adaption, mental, social, functional, speech)
1.Traditional treatment (mechanical)
Teach the patient the correct position when sitting down, lying down.
Treatment of the joints of the injured part
Elongation exercises, strengthening exercises and resistance exercises
2. Physical Therapy
Stimulation of the nerve and muscle damaged in the affected area
Different types of stimulation include: FES, IDC, IF, TENS by case and status.
Cold laser rays, long wave, us, sad
Running and walking exercises (slow-fast)
Bio feed back devices to make the patient more aware of the movement of the affected limb to develop its movement through brain-reaching gestures or the use of mirrors
3. Advanced Devices (Third Line of Treatment)
(non-invasive brain stimulation (rtmsbrain stimulation device
Non-surgical interventions to stimulate the spinal cord epidural stimulation
Mechanical pull device for the spine exposed to disc slippage, nerve pressure and spin MED
VR software (electronic games) for the virtual world helps to move the affected part.
4. Treatstroke complications
Shoulder dislocation
Inflammation and rupture of tendons
Fluid aggregation and swelling
Treatment of spasms (muscle-tendon) and includes injection of local needles using pharmaceutical substances (BOTOX) or Chinese needles.
Bladder weakness and lack of control
Stop speaking or difficultto find words.
Post-stroke depression.