Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
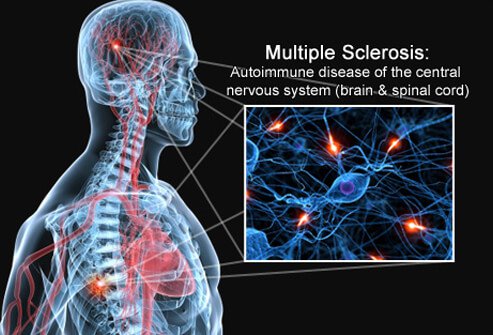
The Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic disease of the central nervous system in which the immune system is involved.
It attacks the myelin sheath that surrounds the nerve fiber, which is responsible for transmitting impulses in the brain and spinal cord. At various sites in the nervous system where myelin has been destroyed, plaques of hardened tissue (sclerosis) appear, and nerve conduction is impaired.
Although it initially takes the form of outbreaks, with exacerbations and remissions, it often evolves into a progressive form or appears with stable neurological sequelae that accumulate over time. The clinical manifestations are variable and depend on the location and extent of the lesions. The plaques, which can be located in the spinal cord, brain and cerebellum, produce a variety of signs and symptoms: loss of strength, fatigue, disorientation, visual disturbances, sensory disturbances, sphincter dysfunction, sexual disorders, cognitive and emotional disorders.
Although the course of multiple sclerosis can be adjusted using the latest pharmacological resources, the diagnosis and treatment of complications is complex and requires the participation of an interdisciplinary team, with different specialists, working together to unify individual treatments in a plan that addresses the patient’s deficits.
In general, treatment is done to:
Emergency treatment (hospital recital)
Drug treatment after the period of stability of the patient’s health, which includes:
Treatment of blood pressure and diabetes
Internal brain pressure therapy
Treatment of blood clotting (blood thinners) in the case of ischemic stroke, subject to the necessary conditions
Surgical intervention (blockage of the arteries with the thrombus) where it was greater than 70% less severe and mortality rates with complications of less than 6%.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation
Its purpose is as follows:
Get the injured part back to work.
Reduce dependency on others.
This treatment includes:
(Rehabilitation, physical, adaption, mental, social, functional, speech)
1.Traditional treatment (mechanical)
Teach the patient the correct position when sitting down, lying down.
Treatment of the joints of the injured part
Elongation exercises, strengthening exercises and resistance exercises
2. Physical Therapy
Stimulation of the nerve and muscle damaged in the affected area
Different types of stimulation include: FES, IDC, IF, TENS by case and status.
Cold laser rays, long wave, us, sad
Running and walking exercises (slow-fast)
Bio feed back devices to make the patient more aware of the movement of the affected limb to develop its movement through brain-reaching gestures or the use of mirrors
3. Advanced Devices (Third Line of Treatment)
(non-invasive brain stimulation (rtmsbrain stimulation device
Non-surgical interventions to stimulate the spinal cord epidural stimulation
Mechanical pull device for the spine exposed to disc slippage, nerve pressure and spin MED
VR software (electronic games) for the virtual world helps to move the affected part.
4. Treatstroke complications
Shoulder dislocation
Inflammation and rupture of tendons
Fluid aggregation and swelling
Treatment of spasms (muscle-tendon) and includes injection of local needles using pharmaceutical substances (BOTOX) or Chinese needles.
Bladder weakness and lack of control
Stop speaking or difficultto find words.